Home >> Industries
Precision CNC Machining for Food-Grade Equipment: Building Clean, Durable, High-Performance Parts
When you're designing equipment that blends, cuts, cooks, or packages the food we eat every day, every component must be hygienic, hard-wearing, and dimensionally perfect. Precision CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining delivers that reliability, turning food-safe metals and polymers into parts that survive caustic wash-downs, thermal cycling, and nonstop production shifts—while still meeting strict food grade guidelines.
Why CNC Machining Is Indispensable to Modern Food Processing
Micro-level accuracy. Tolerances down to ±0.01 mm keep blades aligned, filling nozzles leak-free, and sealing jaws airtight—directly impacting yield and shelf life.
Repeatability at scale. Once a program is dialed in, multi-axis CNC machines replicate complex geometries thousands of times with near-zero deviation, perfect for volume production.
Material versatility. From corrosion-resistant 316L stainless to ultra-low-friction UHMW-PE, CNC processes them all without compromising surface finish.
Rapid prototyping & changeovers. Need to tweak a slicer blade profile or increase throughput on a dosing valve? Adjust the CAM file, not the tooling—a critical advantage in a market that prizes agility.
Mission-Critical Components We Machine
Processing Step | CNC-Made Parts | Why They Matter |
Mixing & Blending | Blades, agitators, drive shafts | Uniform particle distribution and reduced batch times hinge on perfectly balanced impellers and vibration-free shafts. |
Slicing, Dicing, Cutting | High-carbon stainless knives, guides, pushers | Razor-sharp edges and precise guides minimize product waste and ensure consistent portioning. |
Conveying & Transfer | Hardened sprockets, gears, rollers | Exact tooth profiles eliminate belt slippage; hard-anodized rollers stand up to sugary or acidic residues. |
Filling & Packaging | Dosing nozzles, sealing jaws | Close-tolerance bores prevent drips; mirror-polished jaws create hermetic seals that extend shelf life. |
Heating & Cooling | Heat-exchanger plates, fins | Uniform wall thickness and tight fit-up promote efficient thermal transfer during pasteurization or chilling. |
Grinding & Milling | Interlocking grinding discs | Even wear patterns produce a consistent granule size, critical for flavor and texture control. |
Dispensing & Dosing | Valve bodies, metering pistons | Lapped surfaces and FDA-compliant O-ring grooves guarantee drop-in, drip-free performance. |
Materials That Make the Grade
316/304 Stainless Steel – Premier choice for direct food contact thanks to corrosion resistance, cleanability, and non-reactivity.
UHMW-PE & PEEK – Low-friction, self-lubricating polymers that reduce contamination risks in bearings and wear strips.
Aluminum (hard-coat anodized) – Lightweight, ideal for non-contact frames or motor housings; protective finish prevents oxidation.
Design & Manufacturing Best Practices for Food Equipment
Hygienic Geometry
Smooth radii, no blind pockets, full weld accessibility. This prevents bacterial harborage and speeds CIP (clean-in-place) cycles.
Surface Finishing
32 µin Ra or better on contact surfaces. CNC polishing and electropolishing cut biofilm risk to nearly zero.
Chemical & Thermal Endurance
Parts must survive caustic detergents at 82 °C wash-down, acid rinses, and blast freezing—often in the same shift.
Traceability & Documentation
Full material certs, lot numbers, and machining logs enable rapid root-cause analysis should a recall ever occur.
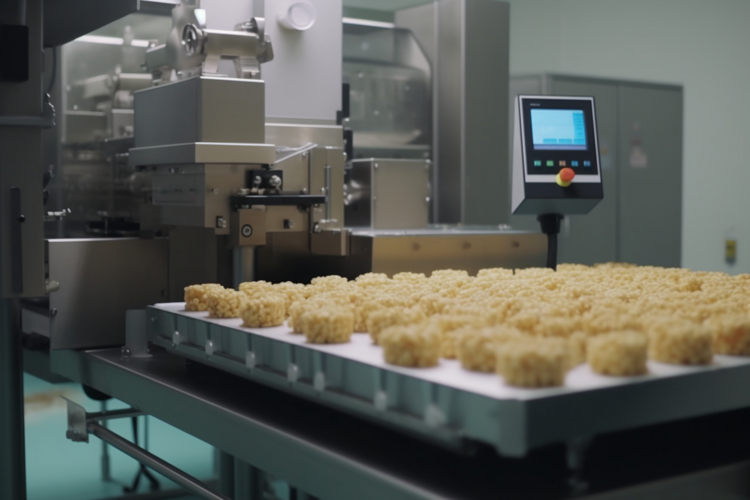

Compliance You Can Count On
Food grade material approvals
ISO 9001- and ISO 13485-certified processes
Bring Your Next Food-Equipment Project to Life
From high-output mayonnaise mixers to precision coffee-pod fillers, Rollyu Precision machines the parts that keep production lines running cleanly and efficiently. Tap into our multi-axis CNC cells, in-house passivation, and 100 % inspection program—and get components that meet every spec on the first delivery.
Let's talk drawings, lead times, and compliance today. info@rymachining.com
Previous: Precision Parts for Lighting