Jan. 29, 2026
Countersinking in Sheet Metal Fabrication: Design Guidelines for Precision Assemblies
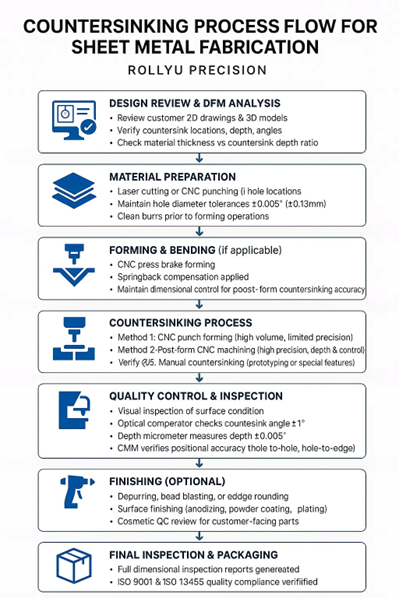
Countersinking in sheet metal fabrication is the process of creating a conical recess at the edge of a hole, allowing a screw or bolt head to sit flush with the surface. This is essential for both aesthetic purposes and to ensure fasteners do not protrude from the finished part, especially in precision assemblies where clearance, appearance, and safety are important.
In precision sheet metal fabrication, adding countersinks allows flat-head fasteners to sit flush with the part surface, improving both the assembly fit and the cosmetic appearance of the finished product. However, unlike in CNC machining where countersinks are produced in thicker, rigid parts with full tool control, applying countersinks in thin sheet metal introduces unique challenges that require careful design and process control.
At Rollyu Precision, we routinely work with customers to optimize countersink features across industries where both appearance and functionality are critical — including medical devices, photonics hardware, semiconductor equipment, automation systems, and aerospace structures.
Why Countersinks Are Used in Sheet Metal
✅ Ensure flush mounting of flat-head fasteners
✅ Prevent fastener heads from interfering with adjacent parts
✅ Improve cosmetic appearance for customer-facing surfaces
✅ Reduce snag points for moving assemblies or operators
✅ Meet clearance requirements in compact, multi-layer assemblies
The Challenges of Countersinking Sheet Metal
Sheet metal differs from machined parts due to its thin material thickness, which limits how deep a countersink can be made without compromising strength or distorting the surrounding area. Some of the key challenges include:
Material deformation from excessive countersink depth
Loss of structural integrity if too much material is removed
Difficulty in controlling angle and depth with punching methods
Positional inaccuracy if not properly fixtured during forming
Increased risk of cracking in hard or brittle materials
Recommended Design Guidelines for Sheet Metal Countersinks
To achieve both precision and manufacturability, the following design rules should be followed when applying countersinks in sheet metal parts:
Design Element | Recommendation |
Minimum Sheet Thickness | At least 2× the countersink depth |
Maximum Countersink Depth | No more than 50% of material thickness |
Countersink Angle | Match fastener standard (typically 82°, 90°, or 100°) |
Flat-to-Countersink Clearance | At least 0.5× material thickness |
Hole Center Tolerance | ±0.005" (±0.13mm) |
Countersink Depth Tolerance | ±0.005" (±0.13mm) |
Avoid Near Bends / Edges | Keep countersinks clear of formed features |
Tolerance Recommendations for Countersinks in Sheet Metal
Since countersinks are highly sensitive to depth and angle variations, the following tolerances are typically applied in precision sheet metal work:
Feature | Recommended Tolerance |
Hole Diameter | ±0.005" (±0.13mm) |
Countersink Diameter | ±0.010" (±0.25mm) |
Countersink Angle | ±1° |
Countersink Depth | ±0.005" (±0.13mm) |
Hole Position (Location) | ±0.005" (±0.13mm) |
At Rollyu Precision, these tolerances are achievable across a wide range of sheet metal materials including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and specialty alloys used in regulated industries.
How Countersinks Are Manufactured in Sheet Metal
Depending on the production volume, required precision, and part geometry, several manufacturing methods may be used to create countersinks:
Process | Application Details |
CNC Punching with Countersink Tool | Efficient for high volumes; limited depth control |
Post-Forming CNC Machining | Highest precision for critical applications |
Manual Countersinking | Used for prototypes or very small batches |
Multi-Step Forming | Occasionally applied for large countersinks or softer materials |
Industries Where Countersink Precision Matters
At Rollyu Precision, we apply countersinking expertise across industries where tolerance control directly impacts product functionality:
Industry | Application Examples |
Medical Devices | Sterile enclosures, surgical equipment |
Photonics | Optical frames, light path alignment plates |
Semiconductor Equipment | Vacuum chambers, cleanroom panels |
Aerospace | Interior structures, lightweight brackets |
Automation & Robotics | Control panels, moving enclosures |
In each case, controlling both depth and angle of the countersink ensures secure fastening, repeatable assembly, and proper surface alignment.
Common Design Pitfall Example